There are many different ways of categorizing learning styles including Kolb’s model and the Jungian learning styles. Neil Fleming’s VARK model is one of the most popular representations. In 1987, Fleming developed an inventory designed to help students and others learn more about their individual learning preferences.
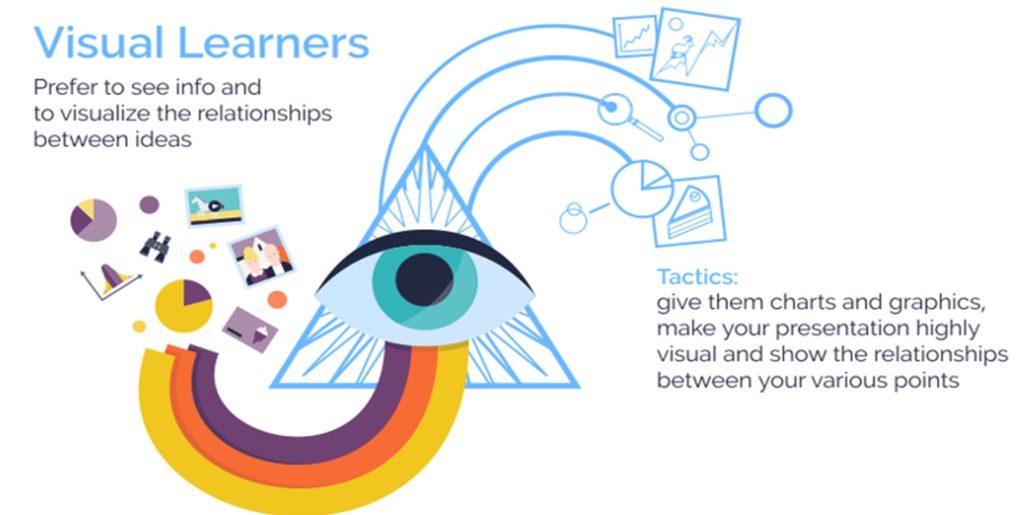
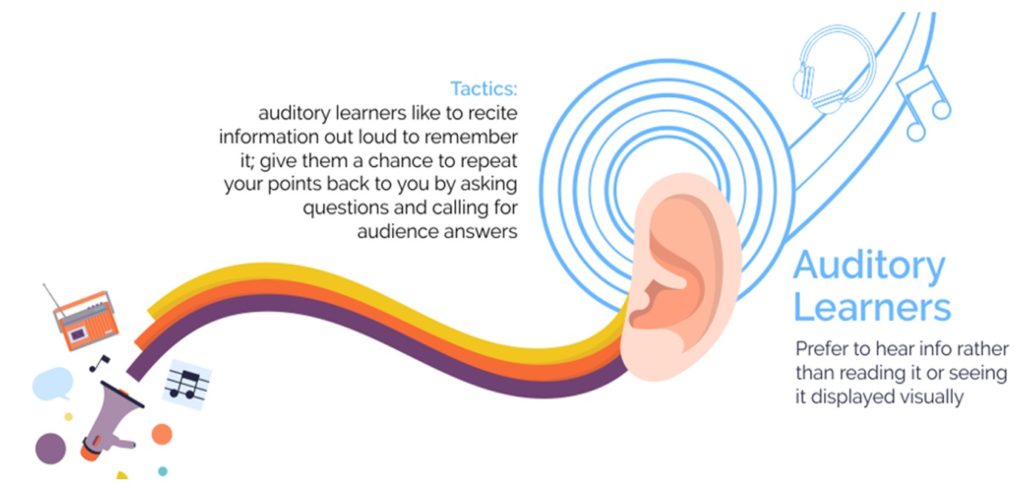
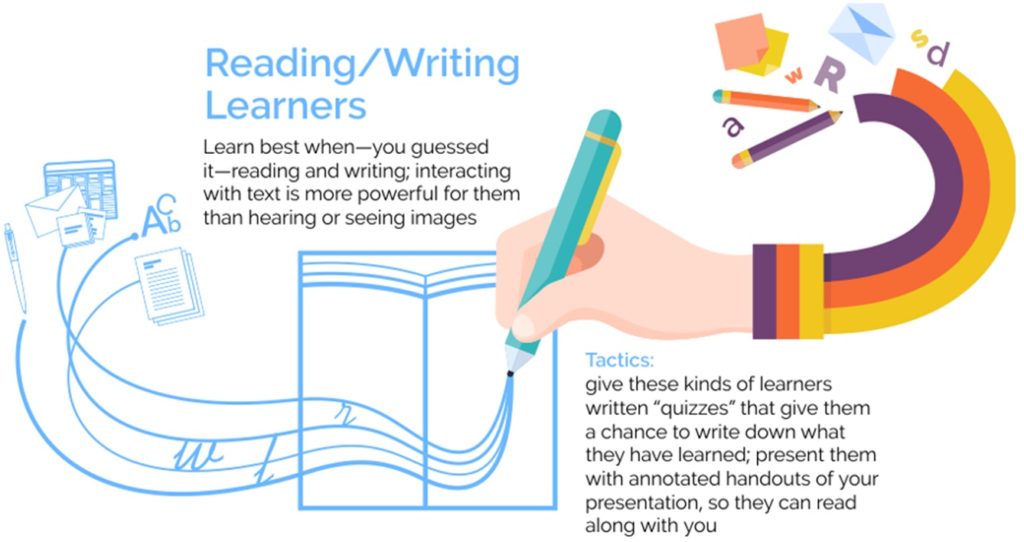
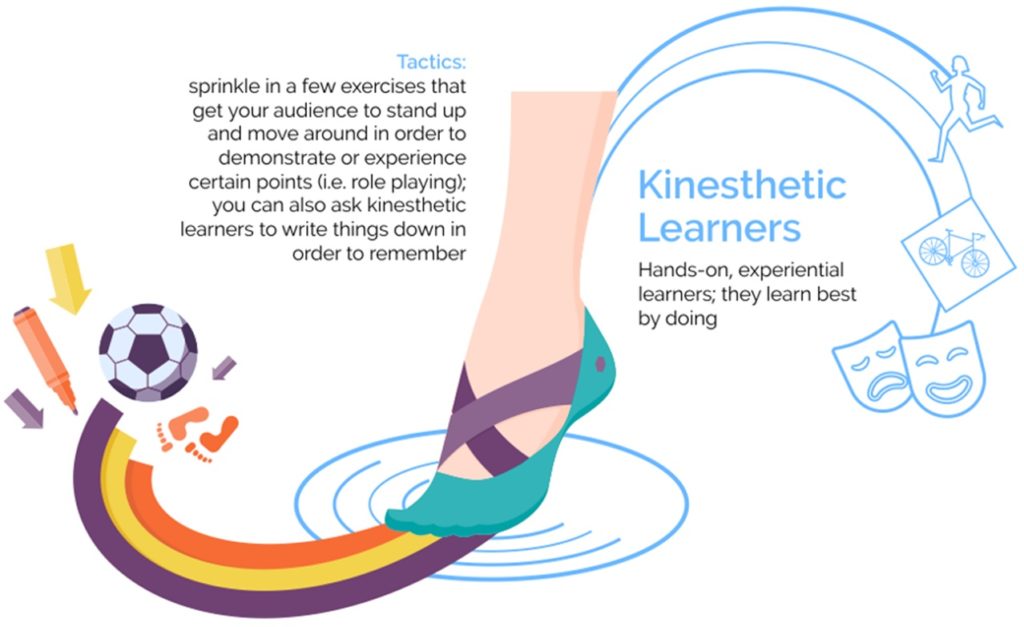
In Fleming’s model, which are often referred to as VARK learning styles, learners are identified by whether they have a preference for visual learning (pictures, movies, diagrams), auditory learning (music, discussion, lectures), reading and writing (making lists, reading textbooks, taking notes), or kinesthetic learning (movement, experiments, hands-on activities).
What Type of Learner Are You?
In order to identify which type of learner people are, Fleming developed a self-report inventory that posed a series of situations. Respondents select the answers that best match their preferred approach to learning.
Example
Imagine that you are learning how to perform a new physical skill such as riding a bike or dancing a certain style of dance. In which way would you learn this skill the best?
- Looking at pictures of people performing the skill
- Listening to an expert explain how to do the task
- Reading about how to perform the task in a book
- Watching someone else perform the skill and then trying it yourself
If you chose number one, then you might be a visual learner. If you would rather listen to someone explain how to do the task, then you might be an auditory learner. Those who would prefer to read written instructions are likely reading/writing learners, while those who would rather gain hands-on experience are most likely kinesthetic learners.
Take a closer look at what each of the VARK learning styles entails.